tsl-textures

TSL Textures
Rotator
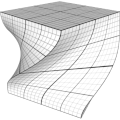
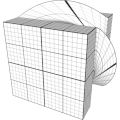
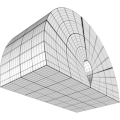
This texture deforms a shape by rotating part of its vertices. The rotation is defined as YXZ rotation of Euler angles around a 3D pivot point used as rotation center.
The selection of affected vertices is set by a imaginary thick planar layer. Vertices “below” the layer are not affected, vertices above the layer are fully affected. Vertices inside the layer are gradually affected depending on how close they are to the “bottom” or the “top” of the layer. The layer is defined by its own pivot point, rotation agles and width.
Hint: use the show checkbox of the online generator to visualize the layer.
Code template
import * as THREE from "three";
import { rotator } from "tsl-textures";
model.material.positionNode = rotator ( {
angles: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
center: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
selectorCenter: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
selectorAngles: new THREE.Vector2(0,0),
selectorWidth: 2
} );
model.material.normalNode = rotator.normal ( {
angles: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
center: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
selectorCenter: new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0),
selectorAngles: new THREE.Vector2(0,0),
selectorWidth: 2
} );
Parameters
angles(x,y,z)– Euler angles for rotation of vertices (in radians)center(x,y,z)– 3D pivot point used for rotationselectorAngles(φ,θ)– spherical coordinates angles for rotation of the selection layer, φ=[0, π], θ=[-2π, 2π]selectorCenter(x,y,z)– 3D pivot point for the selection layerselectorWidth– number for the selection layer width, [0.1, 4]